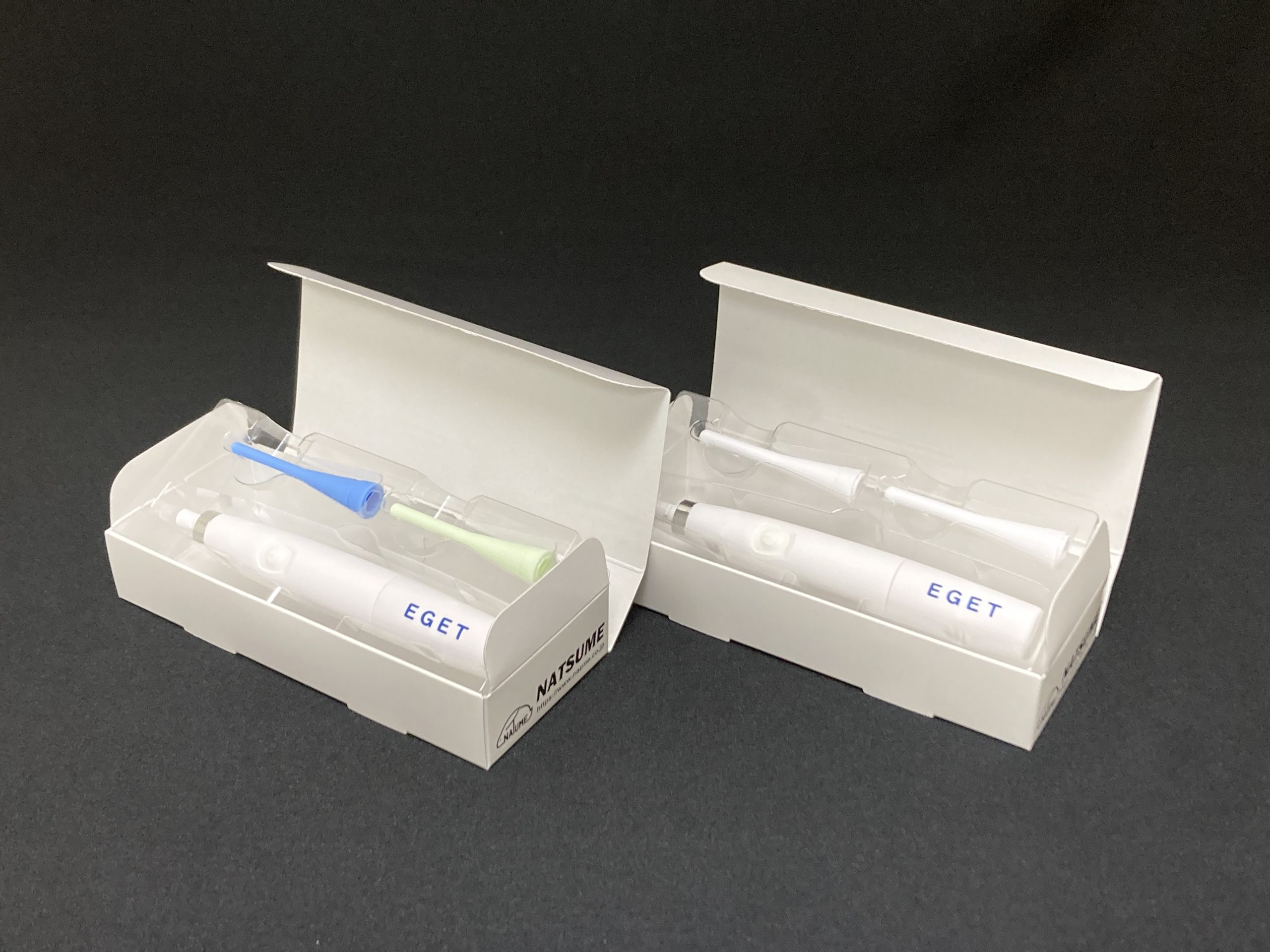
KN-595 EGET
Patent No.7495680※
Inventor
・Osaka Metropolitan University (Formerly of Iwate Univ.), Professor Taketo Kaneko
・Institute for Animal Reproduction
EGET stands for
Easy get next Generation by Embryo Transfer
Conventionally, in order to “produce offspring from transplanted fertilized eggs”,
it was required to create pseudopregnant females by vasectomized males.
“Pseudopregnant mouse and rat production device ~EGET~”
does not require a vasectomized male, achieves artificial pseudopregnancy induction.
This method enables the production of spawn from transplanted fertilized eggs in a compact,
and simple operation. It is expected to reduce the number of animals used and the time required.
In addition, pseudopregnant animals can be produced on the day of transplantation.
It can also be used as a backup for conventional methods.
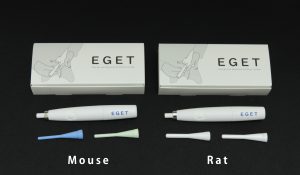
| KN-595-35/40 | KN-595-50 | |
| Target Animal | Mouse | Rat |
| Dimention of Insertion Part |
φ3.5mm×L27mm×1ea (Blue) φ4.0mm×L27mm×1ea (Green) |
φ5.0mm×L27mm×2ea(White) |
| Power | Battery-powered (Battery is not replaceable) | |
| One year of use or used for 100 mice ※Assumed number of uses in case of 30sec x 7 times stimulation |
One year of use or used 250 rats ※Assumed number of uses in case of 30sec x 3 times stimulation |
|
| *Due to the functionality of the product, please use it within the time limit stated above. | ||
*Please comply with local and institutional rules of disposal, or send the entire box of products to us for proper disposal.
*Each EGET is designed to be used 750 times for 30 seconds. The standard stimulation frequency is 30sec x 7 times for mice and 30sec x 3 times for rats.
*The number of times of stimulation is expected to be shortened when the technique is stabilized, so please inquire separately.
*Manufactured and sold by Natsume Seisakusho Co., Ltd. under a patent license agreement.
• Set contents: 1 main unit, 2 tip probes, Instruction manual
*More detailed information on how to use the product![]() is available on the buyers-only page.
is available on the buyers-only page.
【Related Papers】
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36869082/![]()
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35075219/![]()
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32066799/![]()
【Media and Other Publication Information】
2024.05.01 LABIO21_ No.92(p.20~22)_Professor Takehito Kaneko_Japanese
https://www.nazme.co.jp/images/2023/10/LABIO21_No.92_p.20-22.pdf![]()
2024.05.01 LABIO21_ No.92(p.23~26)_Natsume Seisakusho_Japanese
https://www.nazme.co.jp/images/2023/10/LABIO21_No.92_p.23-26.pdf![]()
2023.10.30 Iwate Univ_Japanese
https://www.iwate-u.ac.jp/cat-research/2023/10/005929.html![]()
2023.05.26 Science Japan
https://sj.jst.go.jp/news/202305/n0526-02k.html![]()
2023.03.06 Press Release_Japanese
https://www.iwate-u.ac.jp/upload/a4c7844421e0e1688b6f3a296b34f044.pdf![]()

 click image
click image